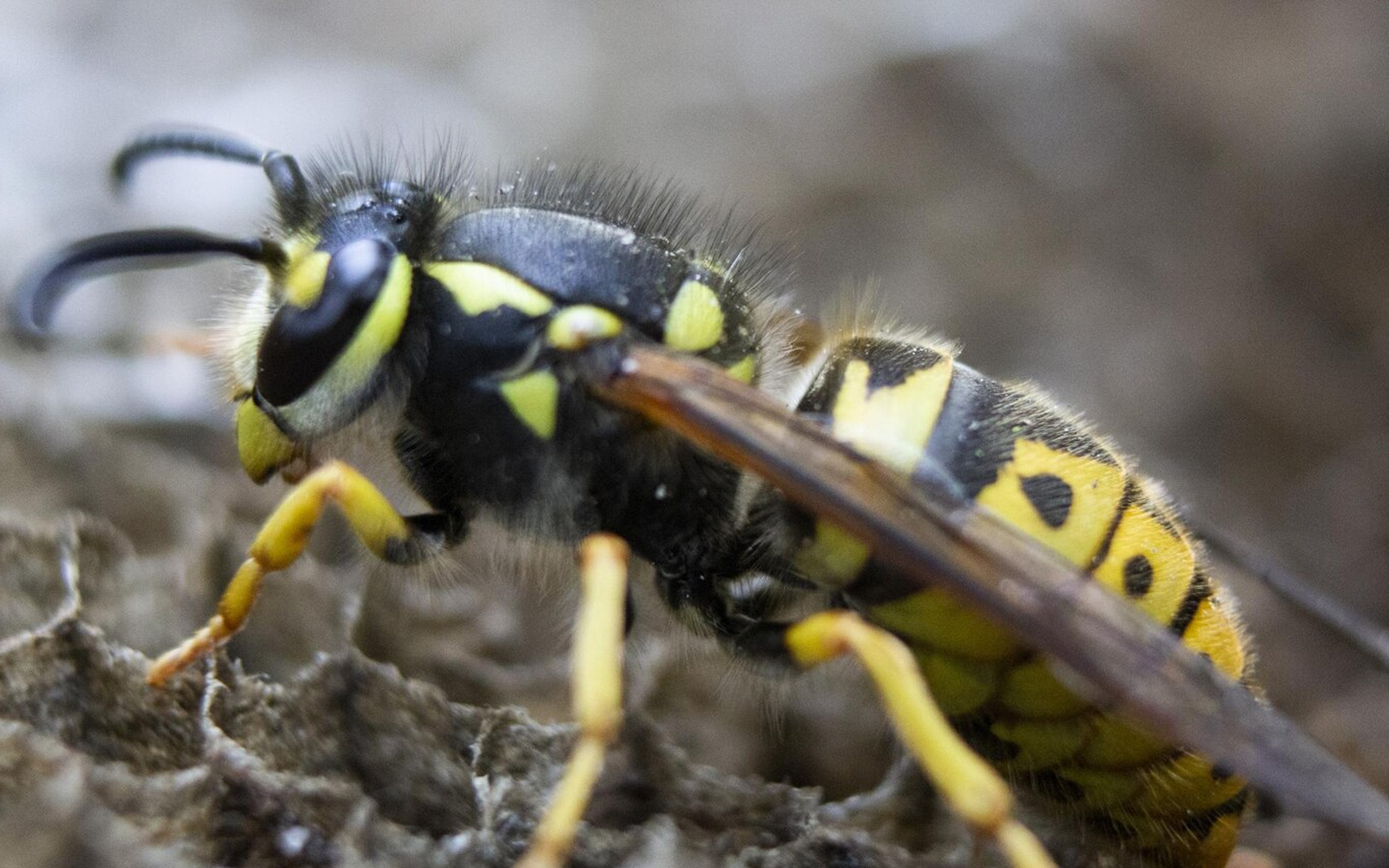
The world’s largest hornet, known for its dangerous sting and ability to decimate an entire beehive within hours, has officially been declared eradicated in the U.S.
This announcement comes five years after the invasive species, Vespa mandarinia, was first spotted in Washington state near the Canadian border. The news was reported early Thursday by the Associated Press.
On Wednesday, Washington State’s Department of Agriculture, in collaboration with federal authorities, confirmed the successful eradication of the hornet, commonly referred to as the “murder hornet.” Officials noted that no sightings or detections of the northern giant hornet have been reported in Washington since 2021.
This achievement was made possible through extensive efforts involving local residents, researchers, and government agencies. Residents participated by allowing traps to be placed on their properties and promptly reporting hornet sightings. Researchers captured a live hornet, attached a tiny radio transmitter, and tracked it through the forest to its nest in an alder tree. The nest was destroyed just as queen hornets were beginning to swarm.
“This is a rare day when humans have truly triumphed over an insect,” remarked Sven Spichiger, the state’s pest program manager, during a virtual press conference.
Despite the eradication announcement, Spichiger emphasized that Washington State will remain vigilant. Entomologists continue to monitor traps in Kitsap County, where an unconfirmed sighting was reported in October. However, efforts to capture a specimen in that area have been unsuccessful.
Spichiger also warned about other invasive hornet species. Officials in Georgia and South Carolina are currently combating yellow-legged hornets, while European giant hornets have recently been detected in Spain. “We will stay alert,” Spichiger assured.
Asian giant hornets, which can grow up to 5 centimeters in length, previously garnered global attention in 2013 when they killed 42 people and severely injured 1,675 in China. According to the U.S. National Institute of Health, approximately 72 people die annually in the United States due to stings from bees, wasps, and hornets.